Research
Epigenetics Mechanisms Underlying Brain Sex Differences
In model organisms, mate selection and mating behaviors have been found to be affected by developmental exposure to environmental estrogenic or anti-androgenic chemicals, suggesting that current environmental levels of chemicals could be affecting the health and behavior of the exposed organisms. Our team is striving to understand the epigenetic basis for brain sexual dimorphism, environmentally induced sex-specific behaviors, and neuroendocrine disruption.
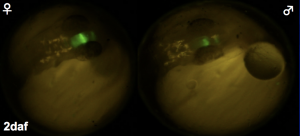
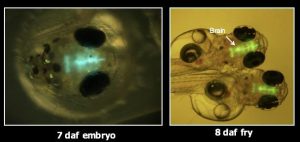
Fig. Cyp19a1b-GFP transgenic medaka.
Related publications
- Bhandari, R.K. et al. Establishment of transgenic lines expressing GFP in the brain cells driven by brain form of aromatase promoter. (in preparation)





